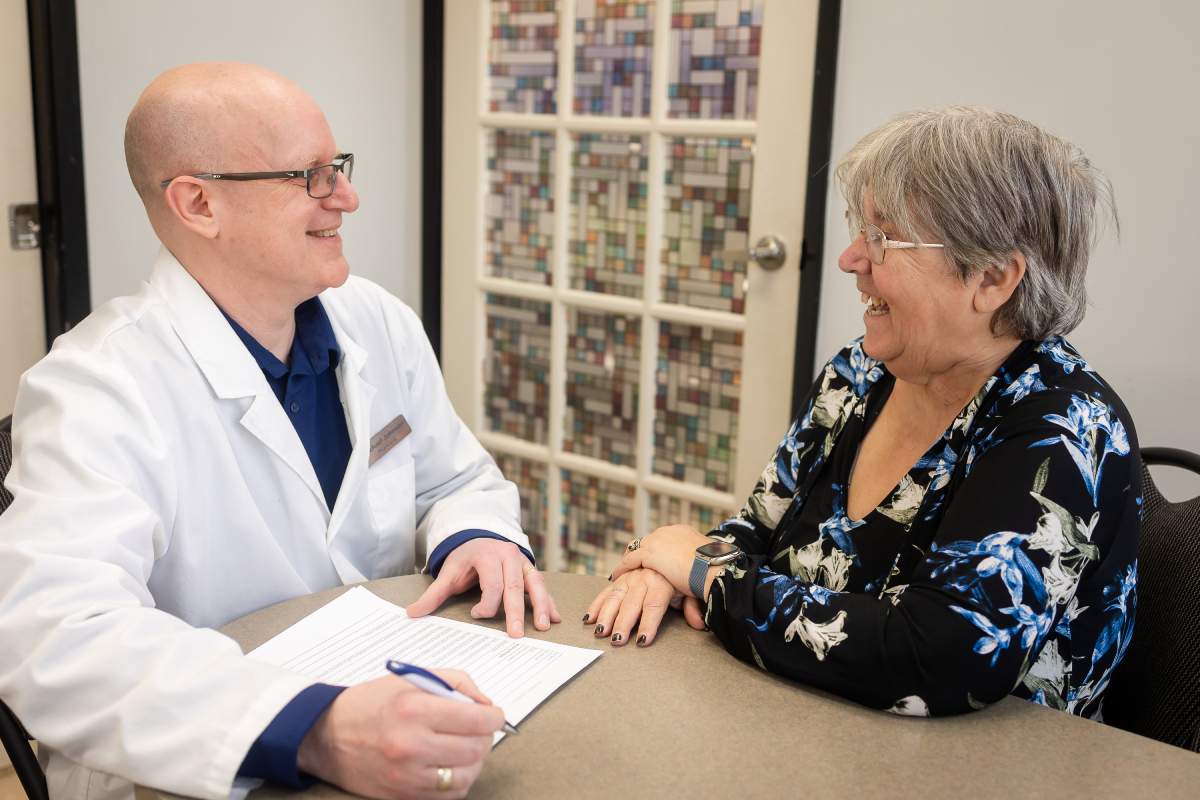
Remembering when and how to take your medications properly can be a challenging task. Read our frequently asked questions or visit Fairway Lackner Pharmasave and ask our pharmacist for assistance.
Many people experience problems with the medications they are taking. These problems can be inconvenient, and may even be dangerous to your health. Find out if you are at risk, and what you can do to avoid medication problems. Ask yourself these questions:
- Do you sometimes forget to take your medication?
- Are you unsure about what your medication is for?
- Do you ever run out of medication before you get a chance to get your prescriptions refilled?
- Do you have trouble swallowing tablets?
- Do you find it hard to open your medication container?
- Do you find taking your medication inconvenient?
- Are you unsure about the side effects of your medication and what to do if any occur?
If you answered “yes” to at least one of the questions: You may be at risk of medication problems. Speak with Fairway Lackner Pharmasave pharmacist about the questions that you answered “YES” to. He or she can help identify any other problems that may exist and suggest ways to deal with them. However, make sure you mention any questions you may have or symptoms that worry you to your pharmacist. Our pharmacist can provide more information and help you deal with any problems that may come up in the future.
Non–steroidal anti–inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are great for inflammatory-type pain. Taking them as directed during painful flare–ups is the key to maximizing their effectiveness. If you need them, the key to safe use is to take the lowest possible effective dose for the shortest period to avoid related health risks you have heard about (i.e. GI bleeding, cardiovascular risk, elevated blood pressure). Even over–the–counter pain medications, such as ibuprofen or ASA, are usually recommended for no longer than 7–10 days and should not be used by those prone to ulcers . Acetaminophen should be considered by those unable to take NSAIDs. Chronic use of acetaminophen is tough on the liver and should be discussed with your physician. Other options include topical ointments and gels, and drug–free choices, such as massage, physiotherapy, and heat and cold application. As a compounding pharmacy,we make pain gels and creams. Please call our pharmacy to learn more.
Generic drugs are identical to or the “bioequivalent” of a brand-name drug in dosage form, safety, strength, quality, how it is taken, performance and intended use.
Absolutely. Both brand-name and generic drug facilities meet the same standards of good manufacturing practices
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are great for inflammatory-type pain. Taking them regularly during pain full flare-ups is the key to maximizing their effectiveness. If you need them, use the lowest possible effective dose for the shortest period of time to avoid any unwanted effects such as GI bleeding, cardiovascular risk and high blood pressure. Even over-the-counter pain medications should not be taken for more than 7-10 days unless directed by your doctor. Always consult with your health professional to make sure these medications are safe for you. Fairway Lackner Pharmasave can make pain gels or creams If one can not take medication by mouth because of stomach problems
Your heart is a muscle that gets energy from blood carrying oxygen and nutrients. Having a constant supply of blood keeps your heart working properly. Most people think of heart disease as one condition. But in fact, heart disease is a group of conditions affecting the structure and functions of the heart and has many root causes. Coronary artery disease, for example, develops when a combination of fatty materials, calcium and scar tissue (called plaque) builds up in the arteries that supply blood to your heart (coronary arteries). The plaque buildup narrows the arteries and prevents the heart from getting enough blood. For more information visit Fairway Lackner Pharmasave.
A stroke is a sudden loss of brain function. It is caused by the interruption of blood flow to the brain (ischemic stroke) or the rupture of blood vessels in the brain (hemorrhagic stroke). The interruption of blood flow or the rupture of blood vessels causes brain cells (neurons) in the affected area to die. The effects of a stroke depend on where the brain was injured, as well as how much damage occurred. A stroke can impact any number of areas including your ability to move, see, remember, speak, reason and read and write.
In some cases, stroke-like damage to the brain can occur when the heart stops (cardiac arrest). The longer the brain goes without oxygen and nutrients supplied by blood flow, the greater the risk of permanent brain damage. Brain injuries can also result in uncontrolled bleeding and permanent brain damage. For more information visit Fairway Lackner Pharmasave
High blood pressure causes the heart to work harder to pump nutrients and oxygen-rich blood to the body. The blood vessels that deliver the blood become scarred and less elastic. Although these changes happen to everyone as they age. They happen more quickly in people with high blood pressure. As the arteries stiffen, the heart has to work even harder, causing the heart muscle to become thicker, weaker and less able to pump blood. When high blood pressure damages arteries, they are not able to deliver enough blood to organs for their proper functioning. This way, organs may become damaged, too. For example, this type of damage can affect the heart, causing a heart attack, the brain, causing a stroke, and the kidneys, leading to kidney failure
Diabetes means that your blood glucose level(sugar) is too high. Your blood always has some glucose in it because the body needs glucose for energy; it’s the fuel that keeps us going. However, too much glucose in the blood is not good for your health.
Your body changes most of the food you eat into glucose. Your blood takes the glucose to the cells throughout your body. The glucose needs insulin to get into the body’s cells. Insulin is a hormone made in the pancreas. The pancreas releases insulin into the blood. Insulin helps the glucose from food get into body cells. If your body does not make enough insulin or the insulin does not work properly, the glucose can’t get into the cells, so it stays in the blood. This makes your blood glucose level high, causing you to have diabetes.
If not controlled, diabetes may lead to blindness, heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, amputations (having a toe or foot removed, for example), and nerve damage. In women, diabetes can cause problems during pregnancy. For more information, please visit Fairway Lackner Pharmasave.